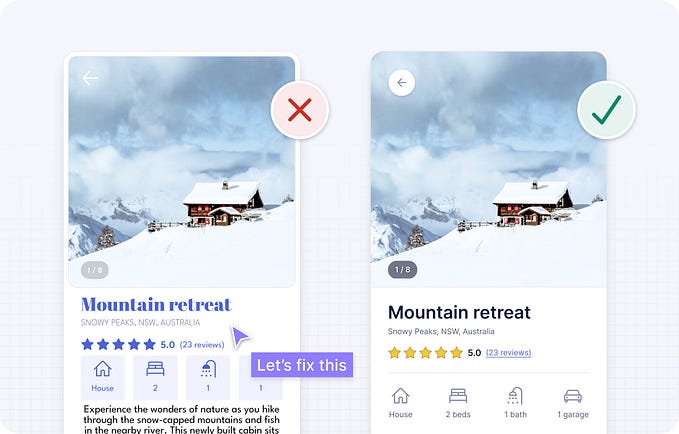
You’re Designing Websites WRONG! Here’s How to Fix It (with Examples)
Different websites serve different needs, and their design must reflect that. In this guide, we’ll explore various website types, their goals, key design considerations, and real-world examples to help you craft memorable experiences.

1. SaaS (Software as a Service) Websites
Purpose:
SaaS websites aim to convert visitors into users by showcasing the product’s value, features, and pricing.
Key Design Considerations:
- Clear Product Messaging: Users should immediately understand what the software does and how it benefits them.
- Simple Onboarding: Easy sign-up, guided product tours, and interactive demos improve user adoption.
- Feature Highlights: A concise and engaging explanation of features with real-world applications enhances credibility.
- Pricing Transparency: Clearly presenting pricing tiers and what each plan offers reduces friction in decision-making.
- Conversion-Optimized CTAs: Strong, action-driven CTAs like “Start Free Trial” or “Book a Demo” guide users toward sign-up.
Example Websites:


2. E-Commerce Websites
Purpose:
The primary goal of an e-commerce website is to sell products effectively. A well-designed e-commerce site improves product discovery, simplifies the checkout process, and builds trust to convert visitors into customers.
Key Design Considerations:
- Show Products Clearly: High-quality images, engaging product descriptions, and clear pricing help customers make informed decisions.
- Make Checkout Simple: A poorly designed checkout process leads to cart abandonment. The design should minimize friction by offering guest checkout, autofill forms, and multiple payment options.
- Build Trust: Including customer reviews, secure payment badges, and return policies reassure potential buyers.
- Easy Navigation: A well-structured menu, filters, and search functionality make product discovery easier.
- Mobile-Friendly: Many customers shop on their phones, so a responsive, mobile-friendly design is essential.
Example Websites:


3. Marketing & Business Websites
Purpose:
A business website serves as a company’s digital presence, providing information about services, values, and ways to get in touch.
Key Design Considerations:
- Clear Value Proposition: A concise and compelling message communicates why a business stands out.
- Social Proof: Client testimonials, case studies, and industry awards establish credibility.
- Strong Call to Action: Whether it’s booking a consultation or subscribing to a newsletter, guiding users toward the next step is key.
- Fast Loading Speed: A slow website can drive visitors away — optimizing images and using efficient code improves performance.
Example Websites:


4. Portfolio or Personal Websites
Purpose:
A portfolio or personal website showcases an individual’s work, skills, and personality. Designers, writers, and freelancers often use these to attract clients and opportunities.
Key Design Considerations:
- Personal Branding: Clients hire people, not just work. Adding personal elements like a unique bio, testimonials, or a blog helps build a connection.
- Make It Visually Appealing — A clean, modern design makes a strong first impression.
- Showcase Your Best Work — Highlight key projects and case studies.
- Art Direction: A visually compelling presentation helps communicate skills effectively. Layouts should be clean, interactive, and engaging.
- Clear Call to Action (CTA): Whether the goal is to attract job offers or client work, clear CTAs such as “Hire Me” or “View My Work” guide users toward the next step.
- Easy Navigation: Ensure visitors can quickly find work samples, about info, and contact details.
Example Websites:


5. Educational Websites
Purpose:
Online learning platforms and course websites facilitate knowledge-sharing through videos, text, and interactive elements.
Key Design Considerations:
- Engagement: Quizzes, gamification, and interactive elements keep learners motivated.
- Navigation & Progress Trackers: Clear progress indicators help users understand where they are in a course and what’s next.
- Accessibility: Designing for different learning styles (audio, visual, and text-based) ensures inclusivity.
- Content Organization: Well-structured courses and easily navigable modules improve the learning experience.
Example Websites:


6. Content or Blog/Media Outlet Websites
Purpose:
Content-driven websites like blogs, magazines, and news platforms aim to provide valuable information in an engaging way.
Key Design Considerations:
- Readability: Typography, line spacing, and contrast play a crucial role in ensuring content is easy to consume.
- Use Images & Videos: Well-placed images and videos break up large blocks of text, making articles more engaging.
- Categorization & Tags: Organizing content with clear categories and tags enhances discoverability and user experience.
- SEO Optimization: Structuring content with proper headings, meta descriptions, and keyword integration helps with search engine rankings.
Example Websites:


7. Community & Forum Websites
Purpose:
These websites enable users to discuss topics, share ideas, and support one another through forums or social networks.
Key Design Considerations:
- User Engagement: Features like upvotes, badges, and leaderboards encourage participation.
- Moderation & Safety: Effective community guidelines and reporting tools ensure a positive environment.
- Thread Organization: Clear hierarchy and search functions help users find relevant discussions.
- Real-Time Interaction: Features like chat, notifications, and mentions keep users engaged.
Example Websites:


8. Non-Profit & Charity Websites
Purpose:
Non-profits use websites to spread awareness, encourage donations, and showcase their impact.
Key Design Considerations:
- Emotional Appeal: Storytelling and impactful visuals connect visitors to the cause.
- Easy Donation Process: A streamlined donation experience increases conversion rates.
- Transparency: Showing financial reports and success stories builds trust.
- Volunteer & Event Information: Providing ways for users to get involved enhances community engagement.
Example Websites:


Conclusion
Web design isn’t just about making a site look good — it’s about creating an experience that aligns with its purpose.
Understanding the different types of websites and their unique design considerations helps you craft experiences that align with user needs.
Whether you’re designing an e-commerce store, a portfolio, or a marketing site, focusing on usability, clarity, and engagement will lead to a successful outcome.
Which type of website do you design most often? Let me know in the comments!
Hey there 👋 I’m Bryson, your go-to UI designer here on Medium.
If you found this article useful, join my free newsletter! I write about UI design topics and share tips and resources to help you improve your skills as a user interface designer.
You can find me on Instagram and Dribbble.
Check out my online store on Gumroad.
Thank you for reading;
Bye for now👋
Check out my other articles: